W.cohn first developed this procedure. The reversible exchange of ions in solution with ions electrostatically bound to some sort of insoluble support medium.
Principle:
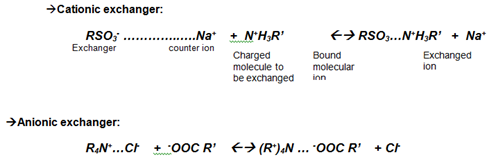
Exchange of ions is the basic principle in this type of Chromatography. In this process two types of exchangers i.e., cationic and anionic exchangers can be used.
Cationic exchangers possess negatively charged group, and these will attract positively charged cations. These exchangers are also called “Acidic ion exchange materials”, because their negative charges result from the ionization of acidic group.

Anionic exchangers have positively charged groups that will attract negatively charged anions. These are also called “Basic ion exchange” materials.
Types of ion exchange resins:
- Two main groups of materials are used to prepare ion exchange resins: Polystyrene and Cellulose.
- Resins made from both of these materials differ in their flow properties, ion accessibility and chemicals and mechanical stability.
- Polystyrene resins are proposed by polymerization reaction of styrene and divinyl benzene.
- A higher concentration of divinyl benzene produces higher cross linkages.
- 5. Polystyrene resins are very useful for separating small molecular weight compounds.
- Increasing the cross linkage increases the rigidity, reduces swelling, reduces porosity & reduces the solubility of the polymeric structure.
- sulfonic acids are strong acids with good proton dissociation ability. By sulfonation process, acidic functional groups are easily attached to nearly every aromatic nucleaus.
- Resins substituted with sulfonic acid groups are strong cationic exchangers.
- To prepare weekly acidic exchanger, carbohydrate groups can be attached to the aromatic rings instead of sulfonic acid group.
- If basic functional groups are introduced, the resin can exchange anions rather than cations. Strong anion exchangers are prepared with a tertiary amine, yielding a strongly basic quaternary ammonium group. Weak anionic exchangers can be prepared with secondary amines, yielding a weakly basic tertiary amine.
Cellulose resins have much greater permeability to macromolecular polyelectrolytes and possess a much lower charge density as compared to polystyrene exchangers.
- Carboxymethyl cellulose (CM-cellulose) – Cationic exchanger
- DEAE cellulose - Anionic exchanger
Preparation of the exchange medium:
There are three steps are of absolute importance:
1) Swelling of medium: (Pre-cycling):
Swelling makes the functional groups to be exposed for ion exchange.
- Swellimg of anion exchangers is usually carried out by treating it. first with an acid (0.5N HCl) and then with base (0.5N NaOH).
- Exactly the reverse is the case with cationic exchangers. The matrix can be treated with EDTA for impurity eliminations.
2) Removal of very small particles:
These fines will decrease flow rate and unsatisfactory reaction. To remove fines, the exchanger is repeatedly suspended in a large volume of water and after the larger polymers have settle down, the slow sedimenting materials decanted.
3) Equilibration with counter ions:
This is accomplished by washing the exchanger with different reagents depending upon the desired counterion to be introduced.
- NaOH –> counter ion to be introduced is “Na+”
- HCl –> counter ion to be introduced is “H+”
- NaNO3 –> counter ion to be introduced is “NO3”
Choice of Buffers:
- Anionic exchange Chromatography should be carried out with cationic buffers.
- Cationic exchange Chromatography should be carried out with anionic buffers.
- The pK of the buffer should be as near as possible to the pH at which the system is buffered. This results in high buffer capacity, which can with stand the local changes of pH in the column easily.
Buffers
PH range
Ammonium acetate 4 to 6 Ammonium formate 3 to 5 Pyridinium formate 3 to 6 Pyridinium acetate 4 to 6 Ammonium carbonate 8 to 10
Practical procedure:
Ion exchange separations are carried out mainly in columns packed with an ion-exchanger. These ionic exchangers are commercially available. They are made up of styrene and divinyl benzene.
DEAE-cellulose is an anionic exchanger, CM-cellulose is a cationic exchanger. The choice of the exchanger depends upon the charge of particle to be separated. To separate anions “Anionic exchanger” is used, to separate cations “Cationic exchanger” is used.
First the column is filled with ion exchanger then the sample is applied followed by the buffer. The tris-buffer, pyridine buffer, acetate buffer, citrate and phosphate buffers are widely used. The particles which have high affinity for ion exchanger will come down the column along with buffers. In next step using corresponding buffer separates the tightly bound particles. Then these particles are analyzed spectroscopically.
Applications:
1. It is extremely used in the analysis of amino acids. The amino acid “Autoanalyzer” is based on in exchange principle.
2. To determine the base composition of nucleic acids. Chargaff used this technique for established the equivalence of Adenine and Thymine; Guanine and Cytosine.
3. This is most effective method for water purification. Complete deionization of water (or) a non-electrolyte solution is performed by exchanging solute cations for hydrogen ions and solute anions for hydroxyl ions. This is usually achieved by method is used for softening of drinking water.
4. Proteins are also successfully separated by this technique.
5. It is also used for the separation of many vitamins, other biological amines, and organic acids and bases.

I am using much similar PRODUCTS, I thank you for the detailed information about this.
ReplyDeletehttp://www.kiranglobal.com
i hope the ion exchange chromatographic technique is independent of sample volume, as long as we use required amount of chromatographic matrix depending upon the dynamic binding capacity and concentration of the sample to be purified.
ReplyDeleteThanks in advance
Bio-Resource
Thank you for your feedback. we will update more info soon. visit again.
ReplyDeleteHi,
ReplyDeleteThe site is about ion-exchange chromatography, Strong Acid Cation Exchange Resin offers you points about the use of it. You will get fresh and contaminated water for your use, thanks...
we are the manufacturer of ion exchange lab equipment / instruments supplier and exporter provider dealer wholesaler in india.
ReplyDeleteThe utility model has the advantages of simple structure and stable and reliable performance, and is an ideal device for wetting tobacco thin slice with carboxymethyl cellulose sodium at present.
ReplyDelete