Electrophoresis is working on the basic principle of migration of charged particles under the influence of electric field. The electrophoresis are mainly TWO types of electrophoresis,
1) Free Electrophoresis (or) Electrophoresis without stabilizing media
2) Zone Electrophoresis (or) Electrophoresis in Stabilizing media
1) Free Electrophoresis:
In this Electrophoresis, Stabilizing media (Agar, Starch, Polyacrylamide)is not using. It has TWO main techniques:
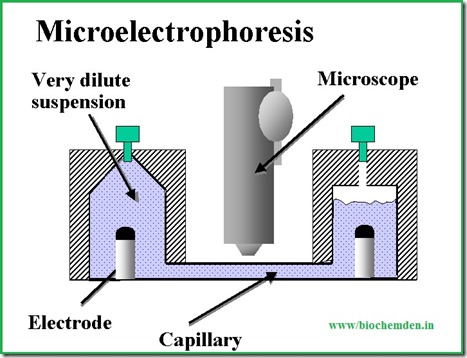
A) Micro electrophoresis:
It involves the observation of motion of small particles in an electric field with a microscope. In modern days this technique is applied only for measuring the Zeta Potentials of cell such as RBCs, Neutrophils and Bacteria etc.
What is this, I want more? See the Details-
Read More: What are the factors affecting on Electrophoretic methods
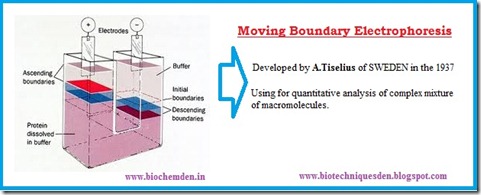
B) Moving Boundary Electrophoresis (m.b.e.):
The technique was first developed by A.Tiselius of SWEDEN in the 1937. this technique is conducting in U-shaped observation cell. It is very popular for quantitative analysis of complex mixtures of macromolecules, especially Proteins.
What is this, I want more? See the Details-
2) Zone Electrophoresis:
KONIG published the first experiment on the use of filter paper as a stabilizing medium in electrophoresis. In this, several stabilizing media are using like Agar, Starch & Polyacrylamide. In this, “Microlitres” of sample can also analyze.
General techniques of Zone Electrophoresis:
- Paper Electrophoresis
- SDS-PAGE
- Iso-electric focusing
Read More: Electrophoresis principle, types, Procedures and Applications.
Best of the best.
ReplyDeleteSimple and informative
ReplyDelete